ITIL Service Operation

This section of the article ensures that readers understand the critical role of Service Operation within the ITIL framework. It outlines the key processes and functions that need to be managed to maintain high service quality and customer satisfaction.
Introduction to Service Operation
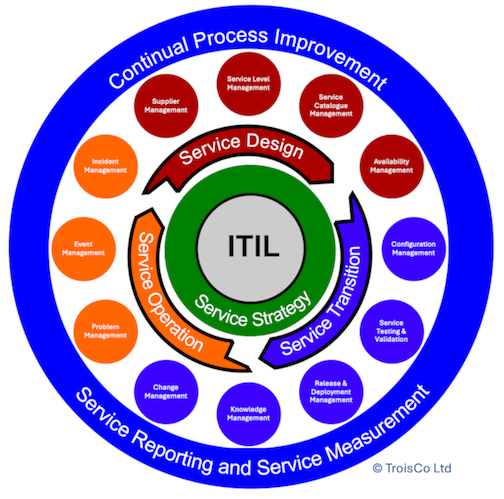
Service Operation is the fourth stage of the ITIL service lifecycle. This phase focuses on the activities, processes, and infrastructure responsible for delivering the services at agreed-upon levels to users and customers. It is where the plans, designs, and optimizations are executed and measured.
Purpose and Goals of Service Operation
The primary purpose of Service Operation is to manage the technology, people, and processes required to deliver and support services. The goals of this phase include:
- Ensuring IT services are delivered effectively and efficiently.
- Maintaining stability in service operations while allowing for changes in design, scale, scope, and service levels.
- Supporting business processes by managing service failures and user requests within agreed service levels.
Key Processes in Service Operation
- Event Management: This process manages events throughout their lifecycle. Event management ensures that operational information is appropriately categorised and communicated, facilitating timely and effective management responses.
- Incident Management: Focuses on restoring normal service operation as quickly as possible following an incident, while minimising impact on business operations and ensuring quality levels and service times are maintained.
- Request Fulfilment: Manages the lifecycle of all service requests from users, ensuring that requests are handled efficiently and effectively, and that user satisfaction is maintained.
- Problem Management: Seeks to minimise the adverse effects of incidents and problems caused by errors within the IT infrastructure, and to prevent recurrence of incidents related to these errors.
- Access Management: Ensures that authorised users are given the right to use a service while preventing access from non-authorised users.
Functions within Service Operation
- Service Desk: Acts as the primary point of contact for users when dealing with service disruptions, requests, and general communications.
- Technical Management: Provides detailed technical skills and resources needed to support the ongoing operation of IT services.
- IT Operations Management: Executes the daily operational activities needed to manage the IT infrastructure. This includes managing the IT infrastructure library and controlling IT operations.
- Application Management: Responsible for managing applications throughout their lifecycle, supporting and maintaining operational applications, and playing an important role in the design, testing, and improvement of applications that form part of IT services.
Challenges in Service Operation
Service Operation faces several challenges, such as:
- Balancing resource allocation between maintaining current IT services and innovating for future enhancements.
- Managing the complexity of modern IT environments and integrating new technologies without disrupting existing services.
- Meeting user demands for immediate and continuous service availability.
Best Practices for Effective Service Operation
- Proactive Monitoring and Control: Implement tools and techniques for proactive monitoring and control to detect and resolve issues before they affect services.
- Effective Communication: Establish clear channels of communication within IT teams and with end-users to ensure everyone is informed of service status and changes.
- Continuous Training and Skills Development: Ensure that IT staff are trained and knowledgeable about the services they support and are equipped to handle new challenges as technologies evolve.
#ITSM #ITIL #ServiceOperation #BestPractices #TechTalk #TechnologyManagement